Microsoft Copilot Studio

Customize Copilot for Microsoft 365
Create custom copilots and GPTs
Use one connected platform
Your copilot, your way
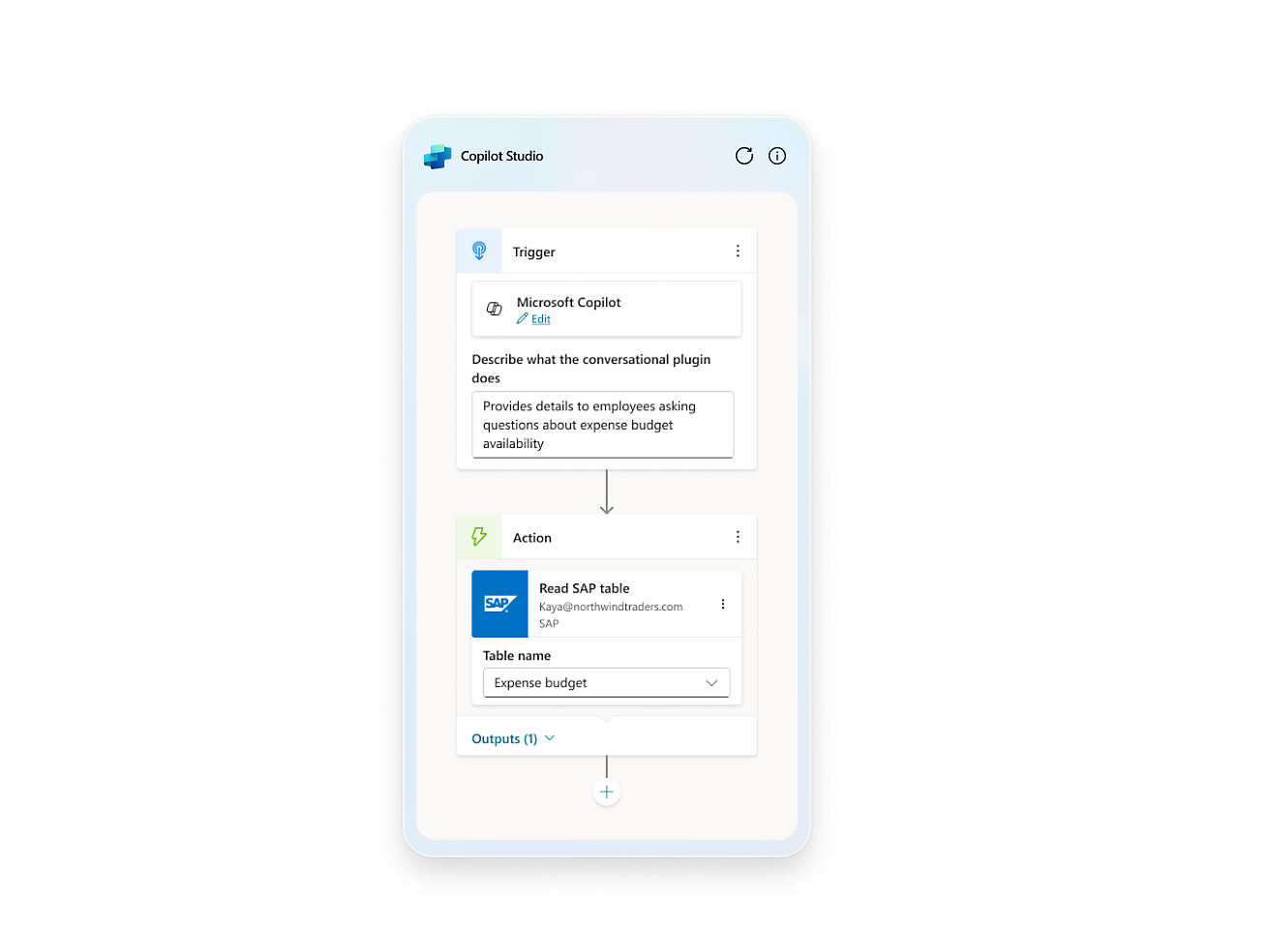
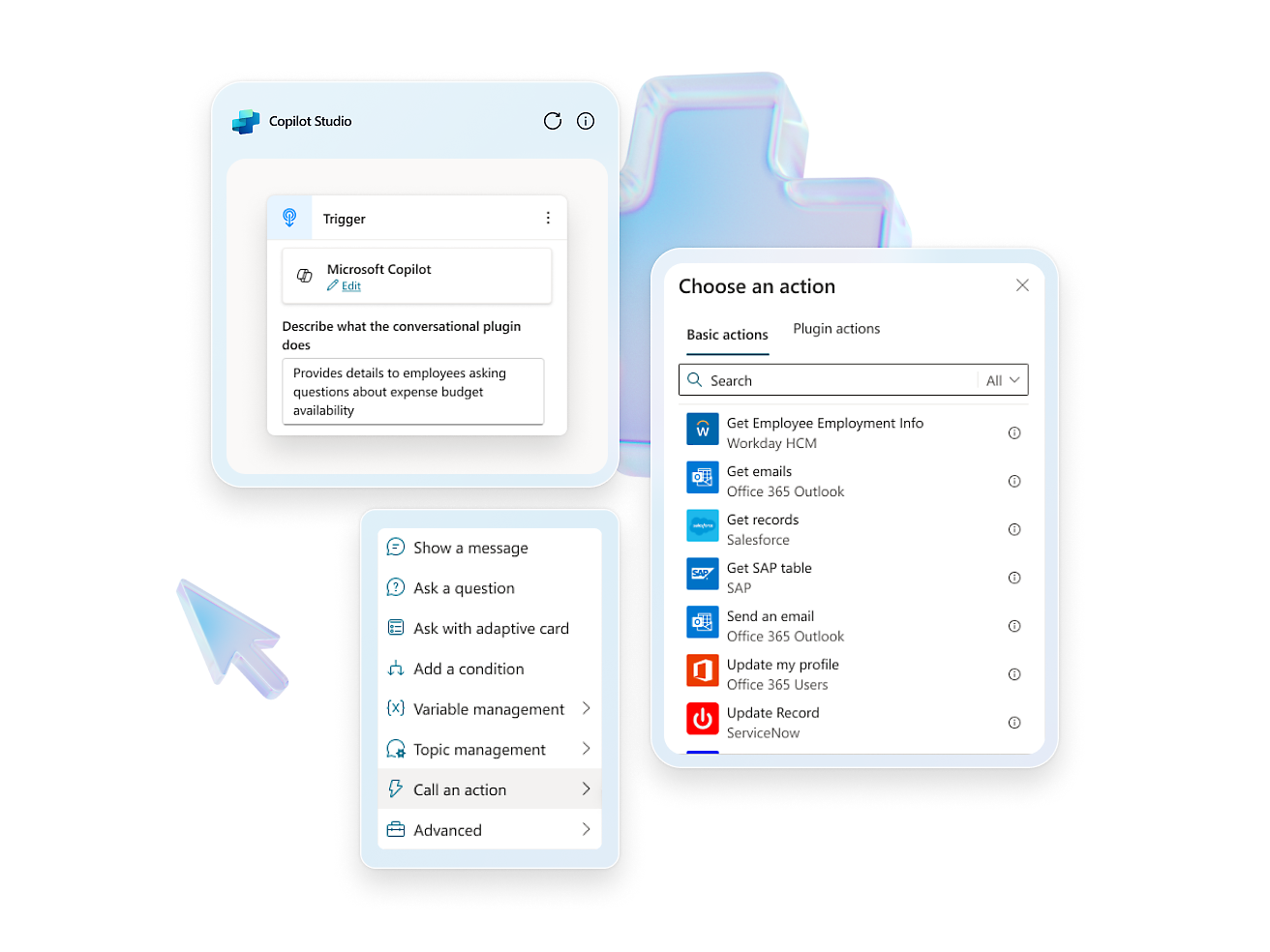
- Design tailored conversations for predictable scenarios that require specific responses, like compliance or regulatory topics.Navigate the intricacies of your processes with ease by using a copilot to automate complex business tasks such as submitting expenses, onboarding employees, and updating benefits.Select, edit, and refine data using over 1,000 prebuilt connectors as plugins, connecting business applications such as SAP and Workday with your copilot.Build and publish custom plugins, GPTs, and prompts, and surface your business data where you need it.
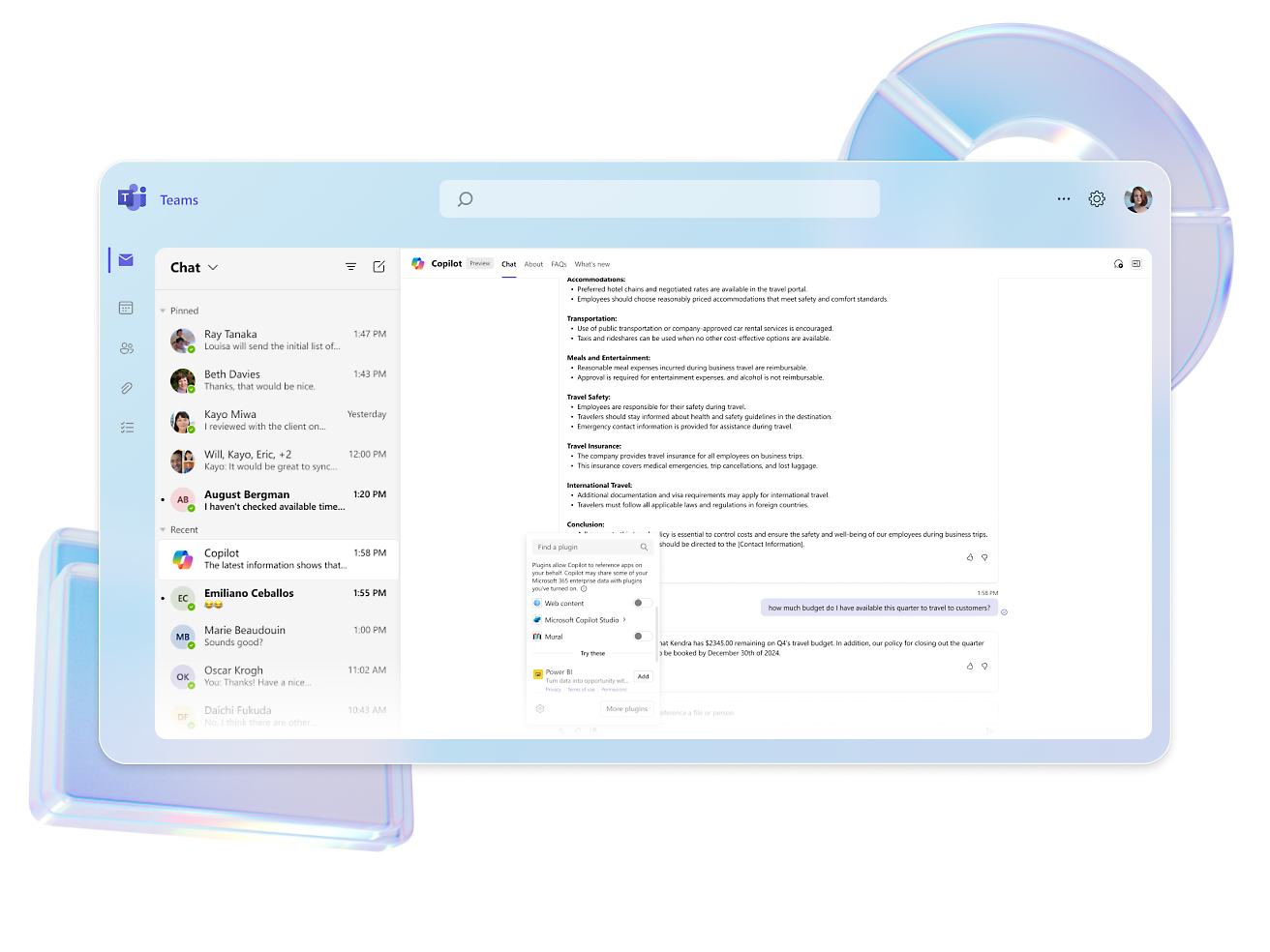
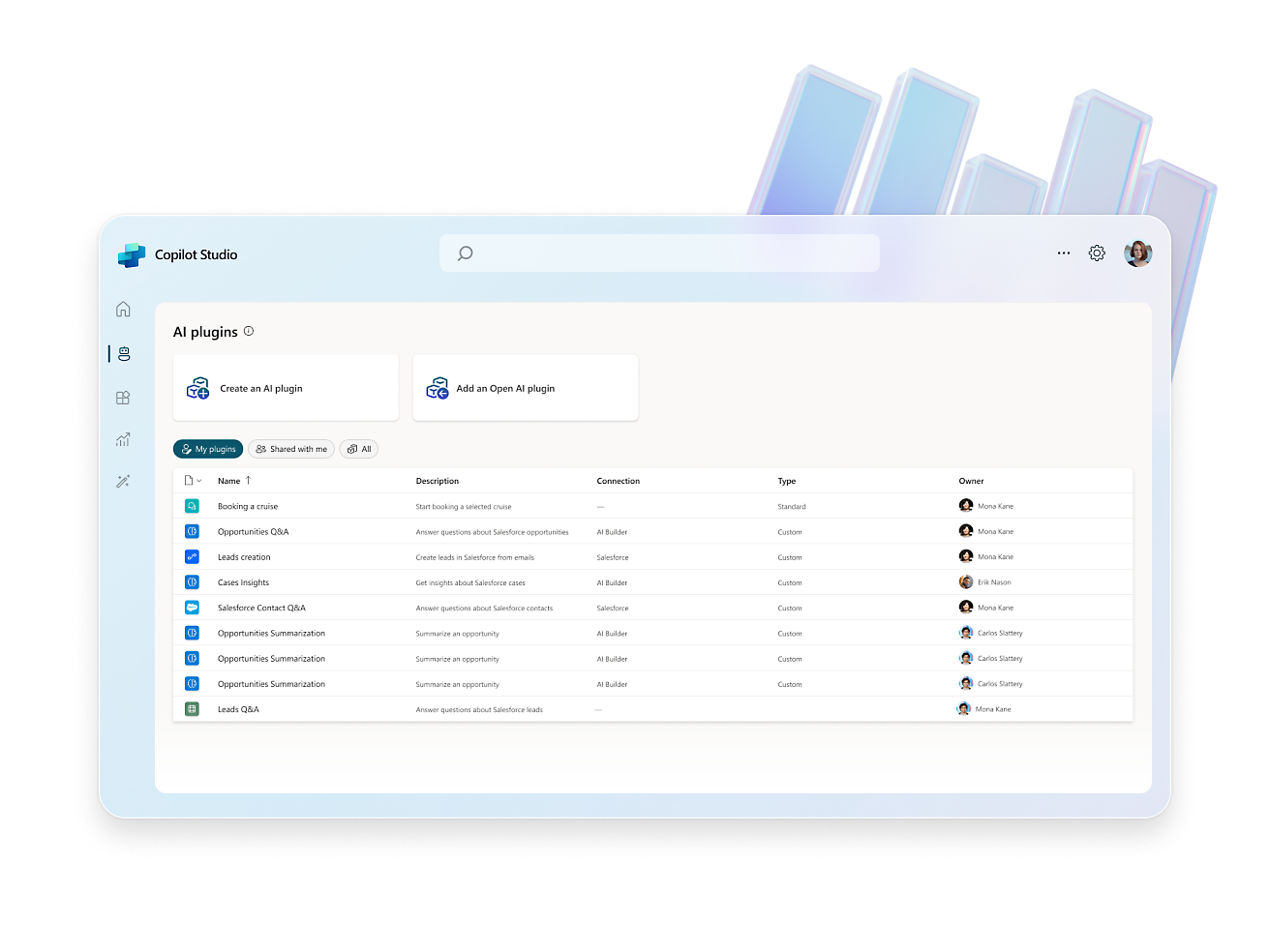
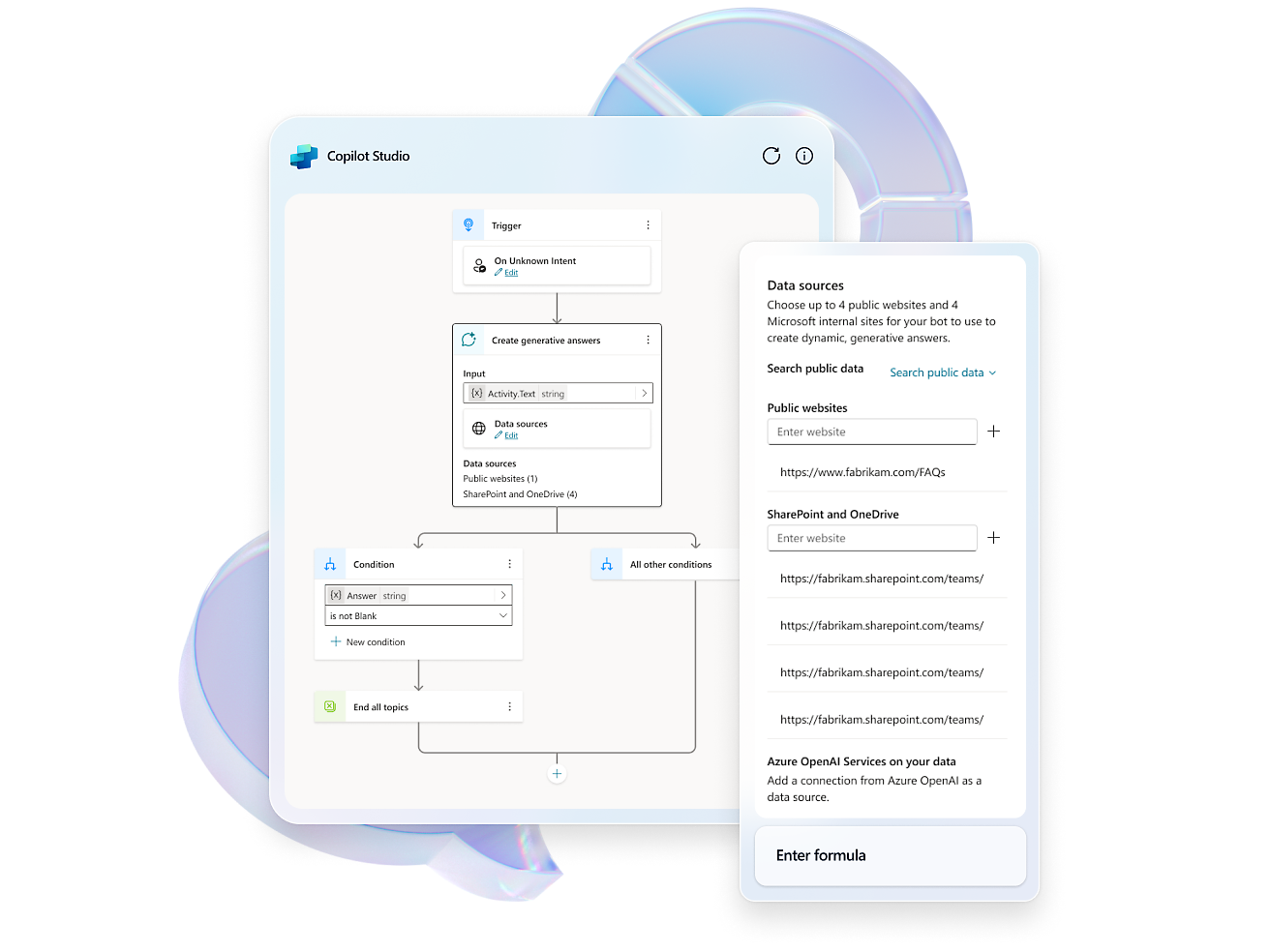
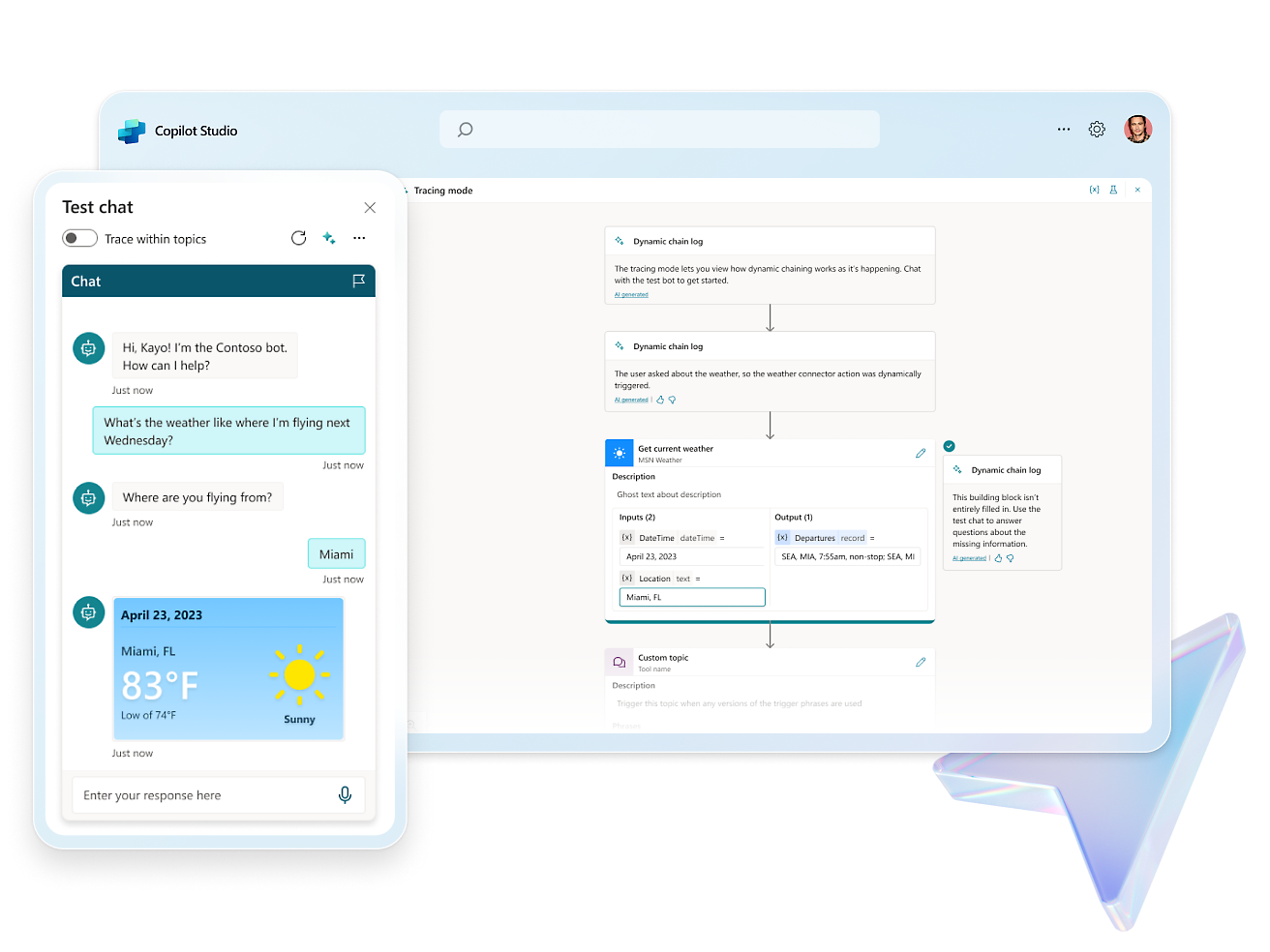
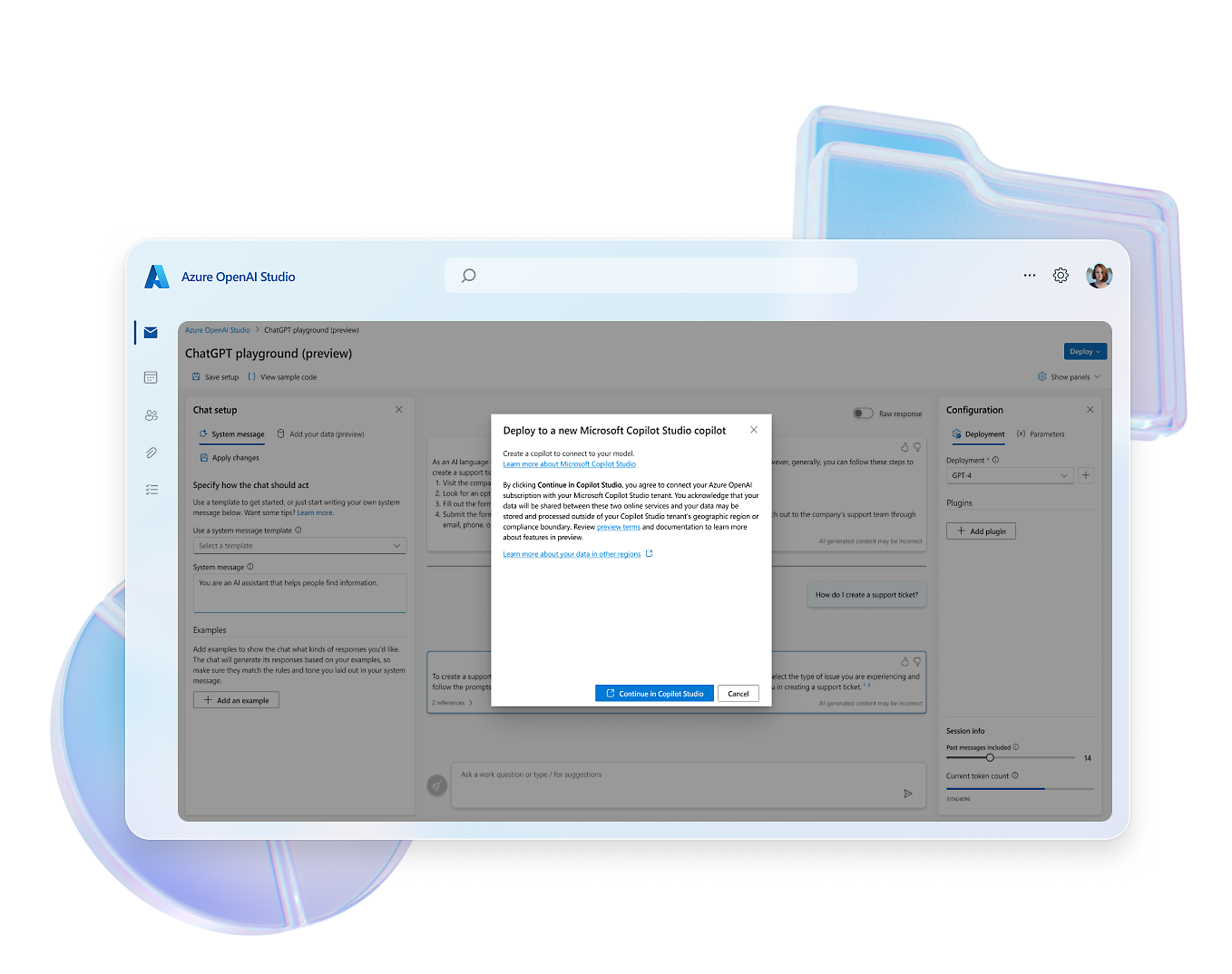
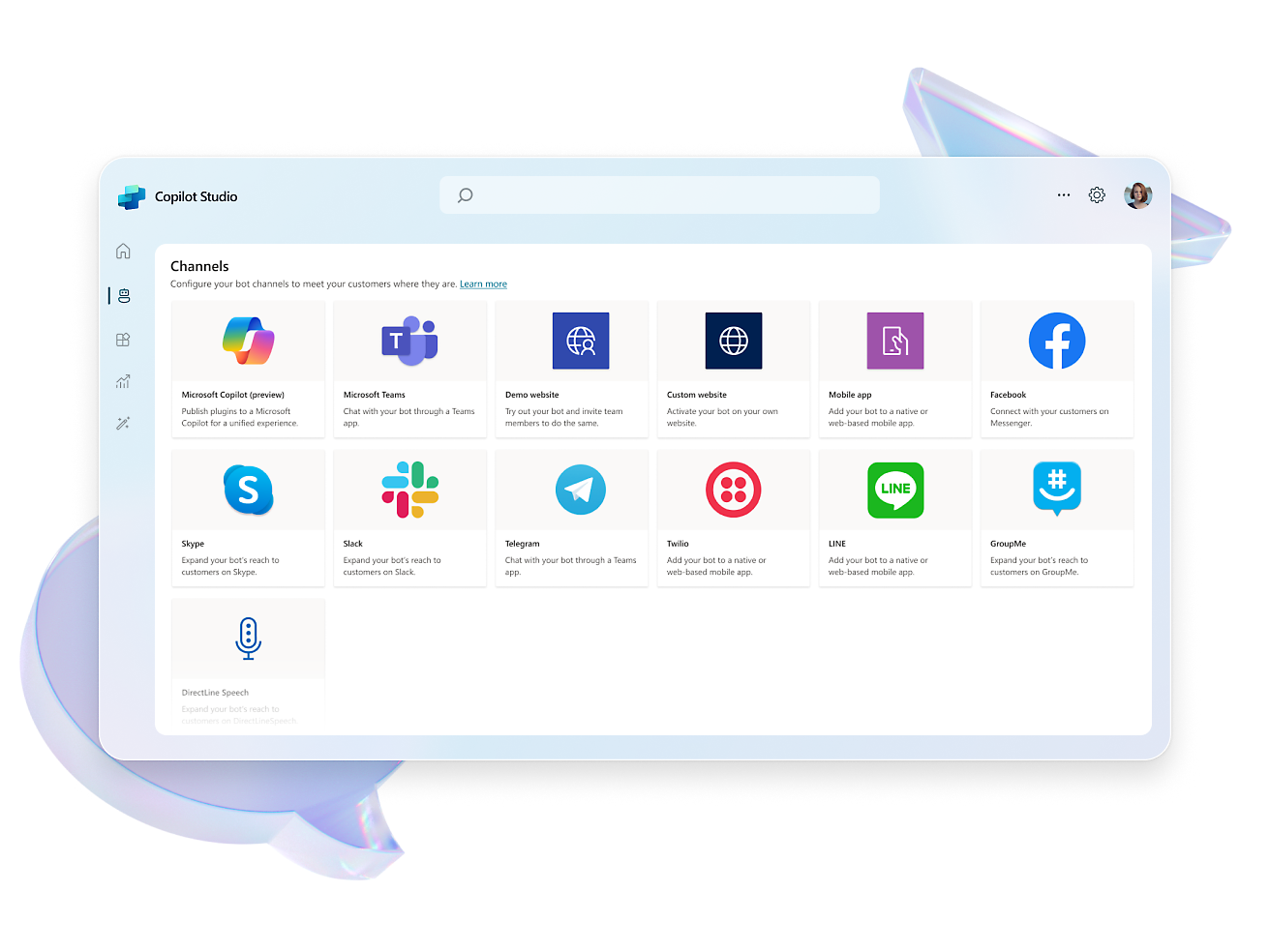
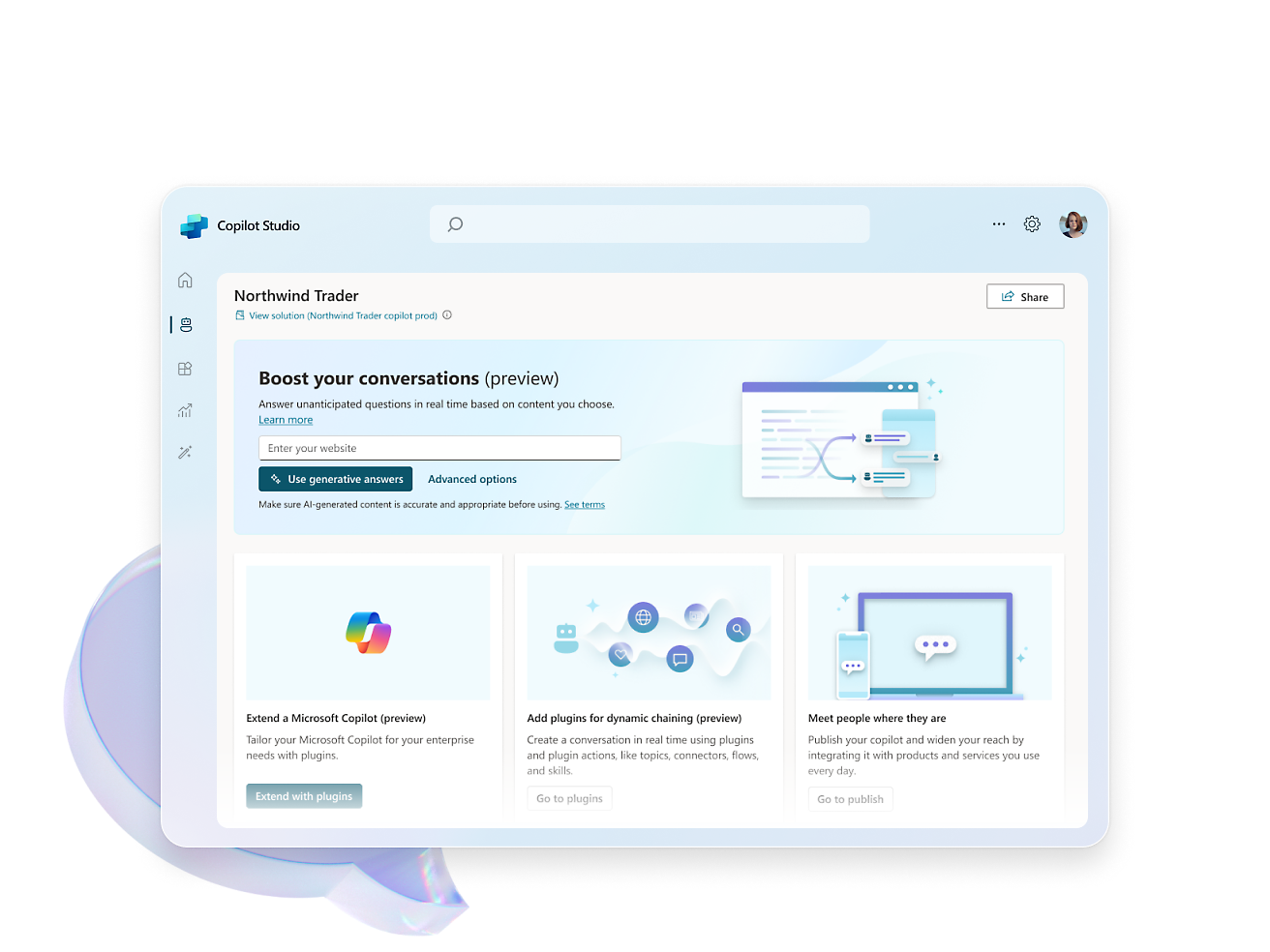
- Elevate your copilot capabilities by pointing your copilot to sources such as websites or internal knowledge bases and watch it answer questions in minutes.Craft, test and chain plugins and GPTs for your copilots by incorporating Microsoft Power Platform connectors, Power Automate flows, custom topics and AI prompts.Configure, train, and connect services within Azure, such as Azure OpenAI Service, knowledge bases, and language models.Easily distribute your copilot across a multitude of channels, including websites and social media, ensuring engagement wherever your users are.
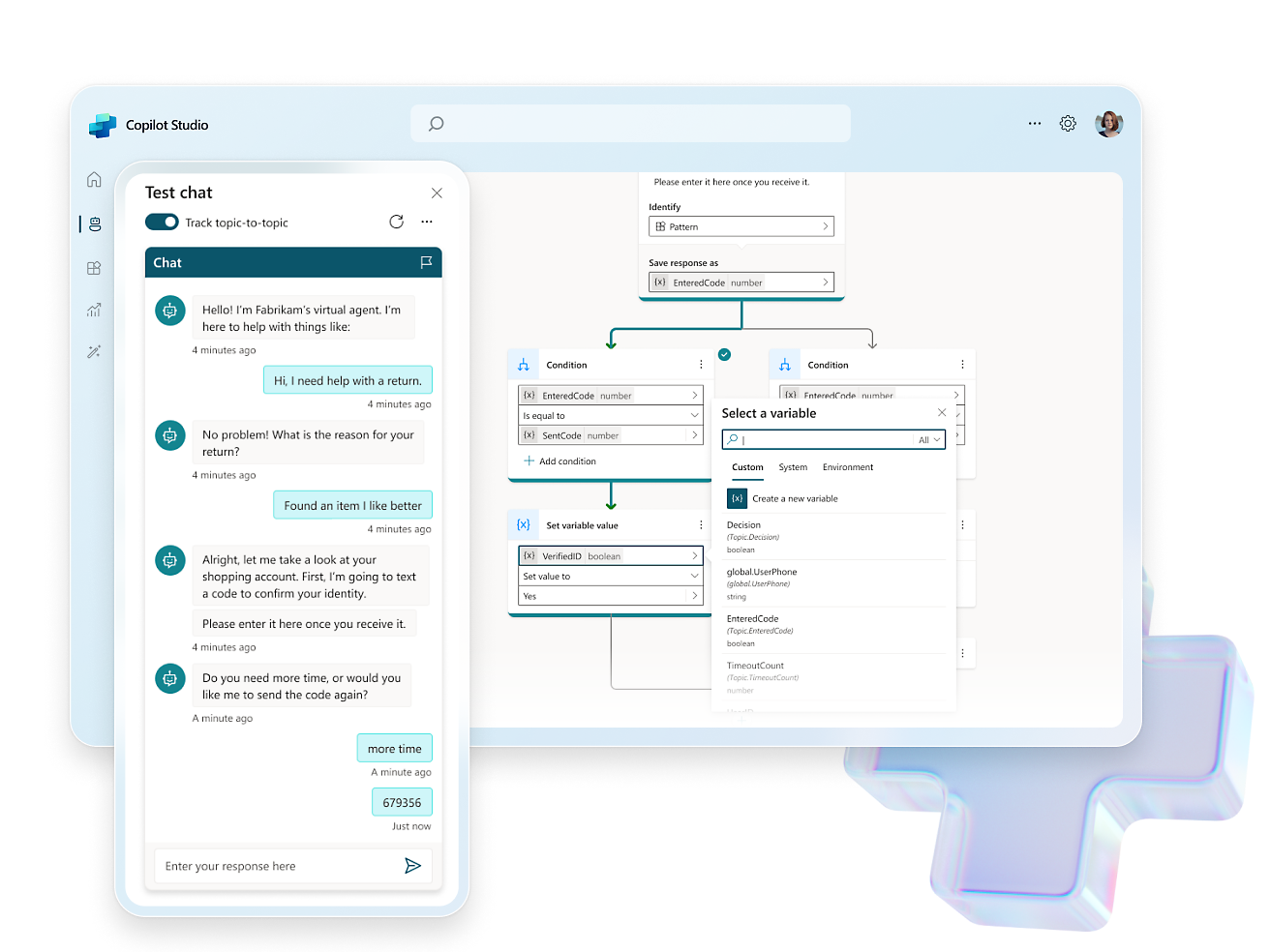
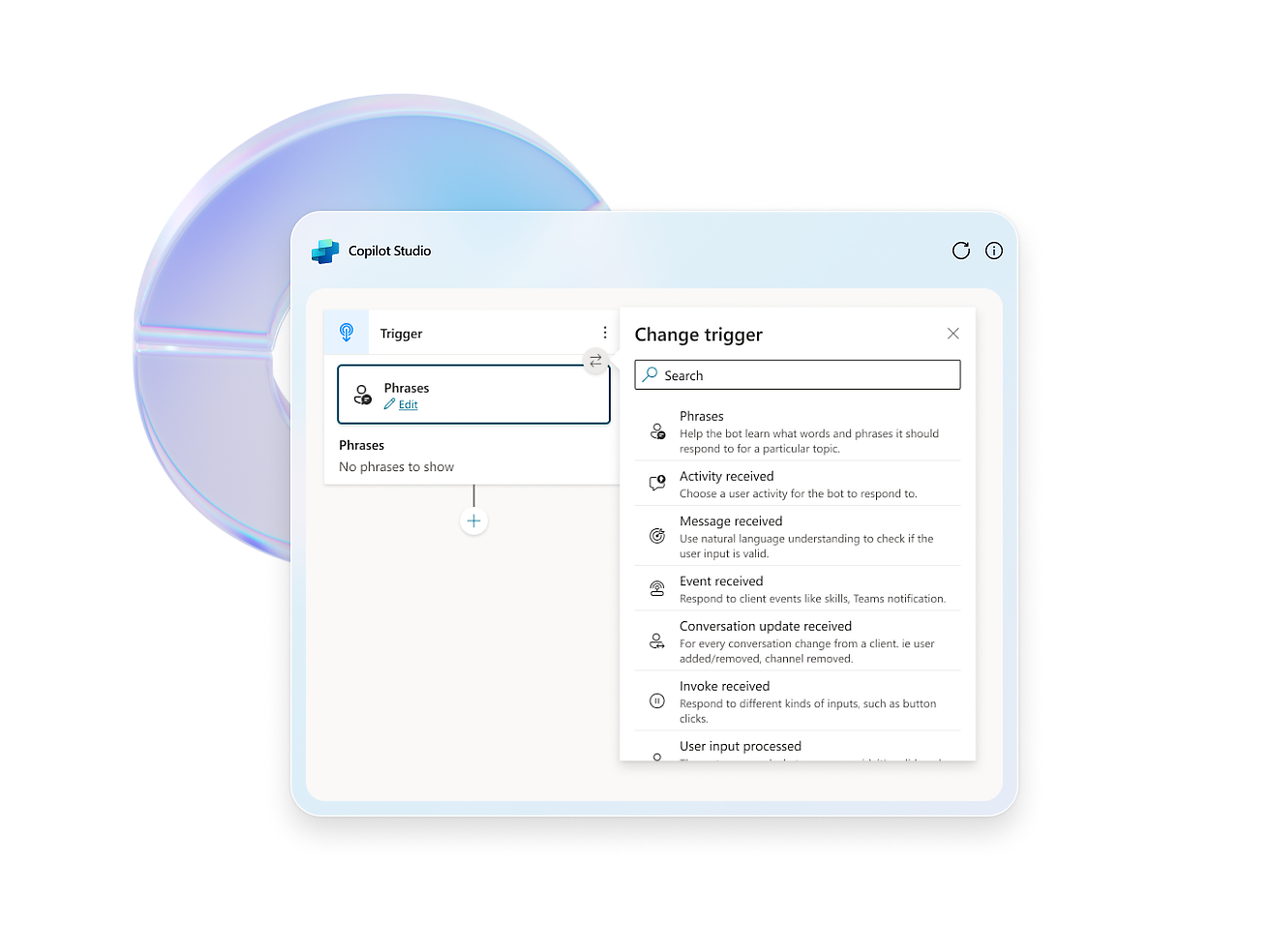
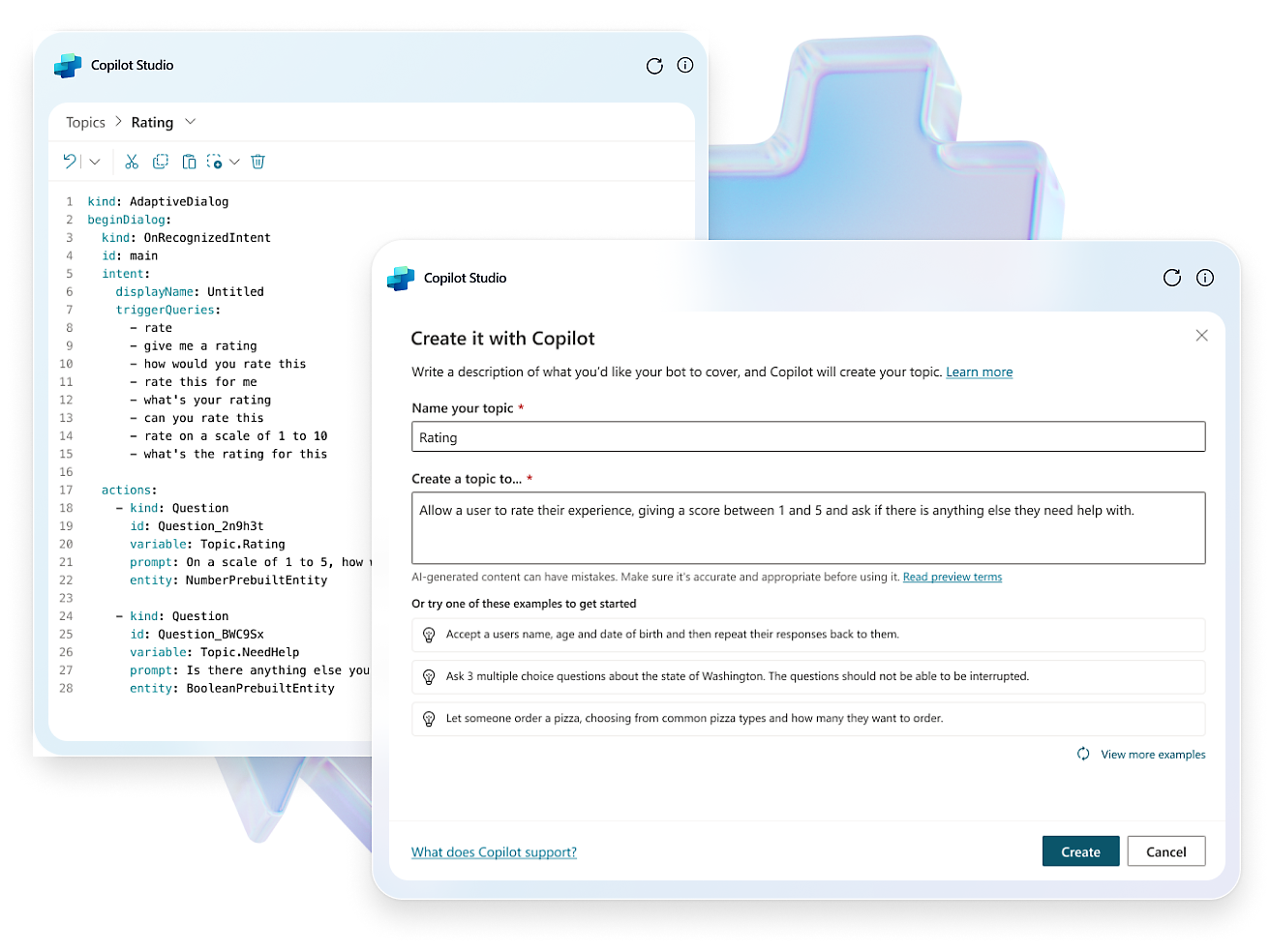
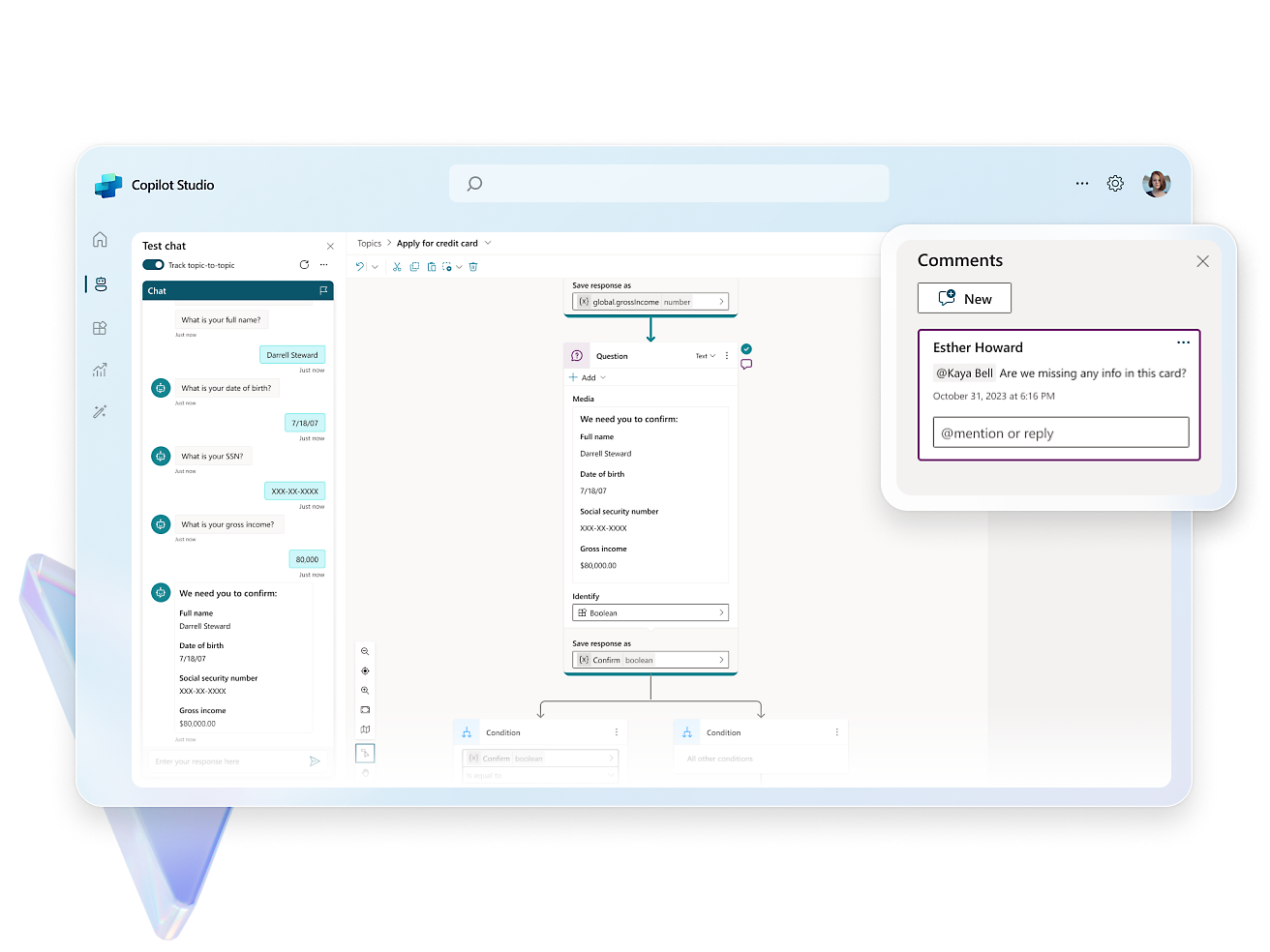
- Use the expansive conversational design tools and graphical interface to create intricate conversations with robust variable management, logic, and responses.Enhance experiences, engage users, and drive customer engagement with rich, dynamic responses, real-time notifications, and personalized interactions.Create copilots using natural language or a graphical interface, or switch to code views.Enhance collaboration with commenting for seamless creation and feedback. Test effortlessly within the studio or share test pages with coworkers.
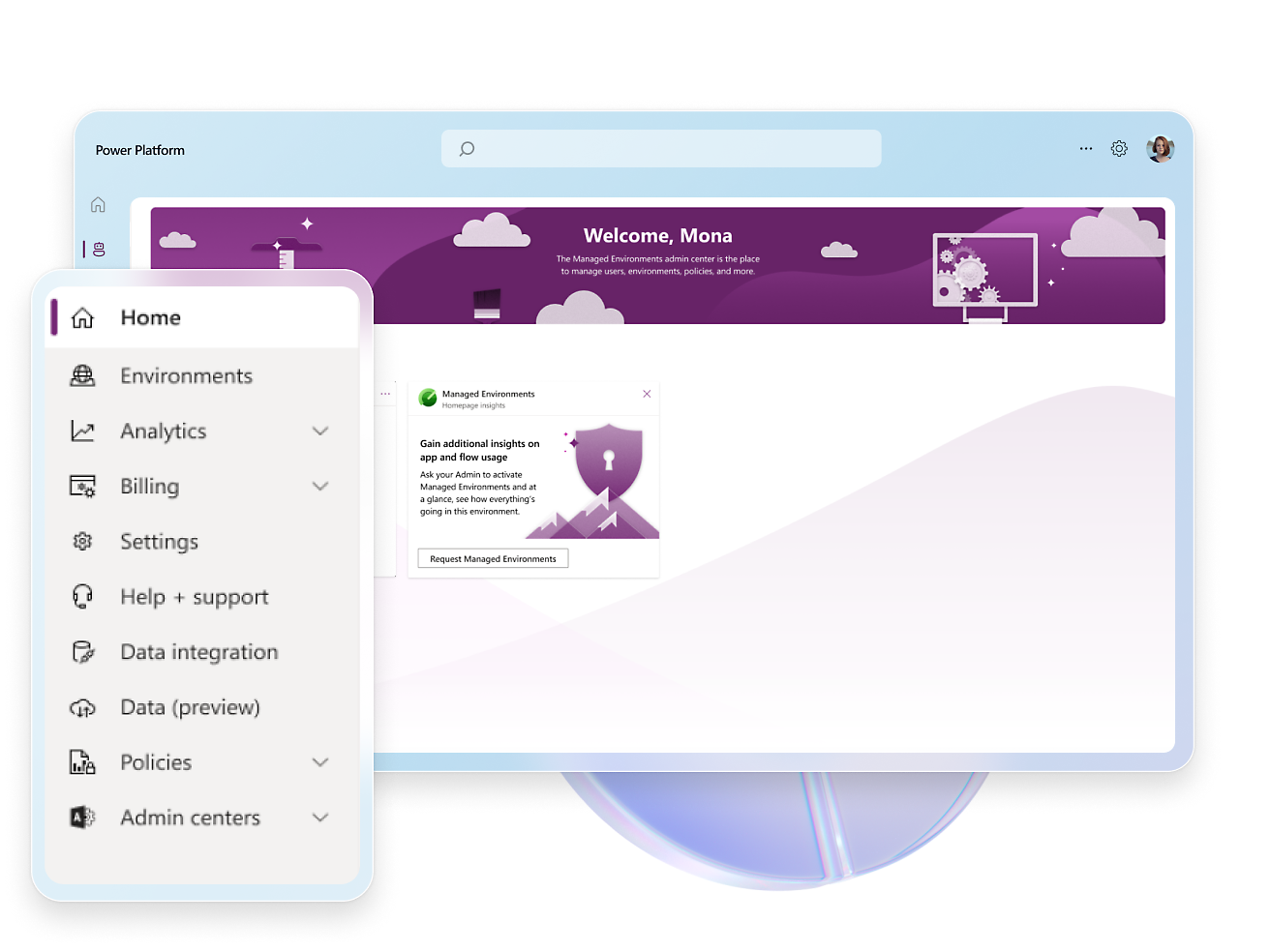
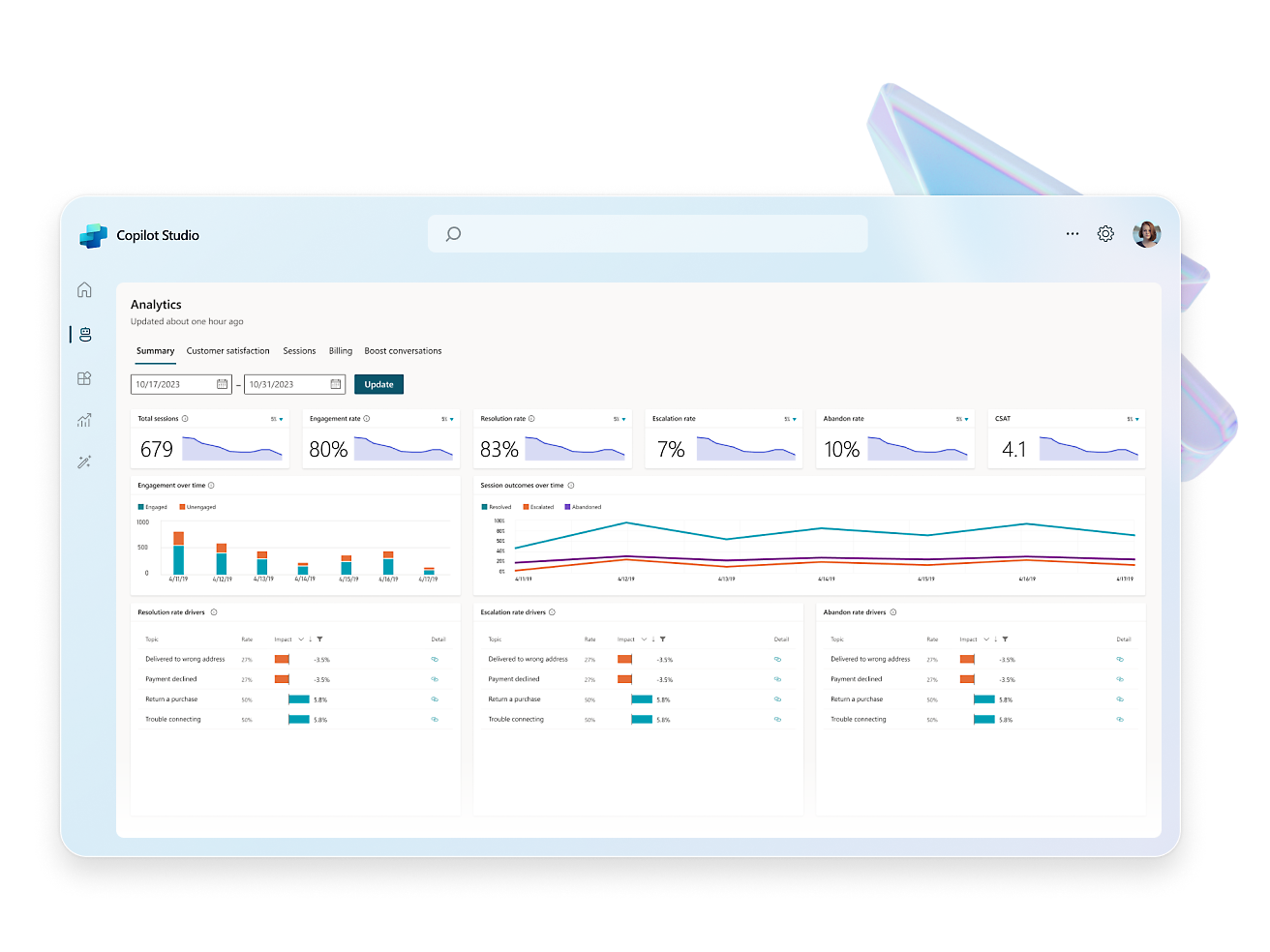
- Establish trust with comprehensive policies, access controls, and tailored environments available within the admin center.Optimize responses and fine-tune your copilot with built-in analytics, including vital key performance indicators (KPIs) that provide invaluable intelligence.Use the benefits of software as a service and eliminate the burdens of infrastructure management, maintenance, and updates, ensuring peak performance for your copilot.Uphold the highest standards of governance, trust, and data control with a dedicated admin center, built using Microsoft responsible AI principles.

Pricing
Microsoft Copilot Studio
- Build and run your own copilots across websites and other channels to serve employees and customers.

Get started with Microsoft Copilot Studio

Empower your workforce with Copilot for Microsoft 365

Explore new ways to work with Microsoft Copilot
Resources and support

Documentation

Community

Support
Additional resources

Introducing Microsoft Copilot Studio

Watch Microsoft Ignite on demand
Frequently asked questions
-
Copilot Studio is an end-to-end conversational AI platform that empowers you to create and customize copilots using natural language or a graphical interface. With Copilot Studio, you can easily design, test, and publish copilots that suit your specific needs for internal or external scenarios across your industry, department, or role.
-
-
You can create, manage, and publish plugins and GPTs from Copilot Studio to Copilot for Microsoft 365 (public preview).
-
Yes, Power Virtual Agents capabilities and features are now part of Copilot Studio following significant investments in generative AI and enhanced integrations across Microsoft Copilot.
-
Generative AI within Copilot Studio is designed to align with Microsoft responsible AI principles, including fairness, reliability and safety, privacy and security, inclusiveness, transparency, and accountability.
Microsoft Copilot Studio